Take Control of Exchange – Managing Shared Mailboxes
The application for managing distribution lists and shared mailboxes in Microsoft Exchange, also known as DSM - Exchange Distribution List and Shared Mailbox Manager, is another solution in our company’s portfolio. This application is primarily aimed at large organizations that use Exchange Server 2010 or 2013 within the organization’s own infrastructure.
Exchange Server is integrated with Active Directory services like no other server – which is, of course, a huge advantage. However, this also comes with consequences. When an administrator creates a mailbox, its attributes from Exchange are added to the Active Directory account. The mailbox, along with its messages, calendar, and tasks, is stored in the database. Each mailbox is always associated with a single AD account, and one account is the owner of the mailbox – this is why a mailbox cannot exist without a user account in the domain.
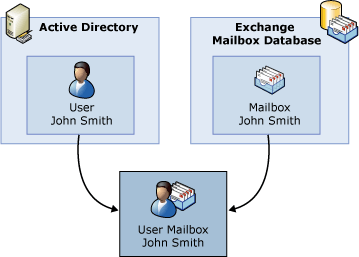
In Exchange Server 2007, Microsoft introduced the functionality of shared mailboxes, though it is not widely known because shared mailboxes cannot be created from the console, but rather from Exchange Shell. Therefore, if, for example, a shared mailbox such as info@ needs to be created for several employees within the organization, you would need to create a mailbox named ‘info’ and assign Full Access permissions to all users who should have access to it. As a result, a user named ‘info’ is created in Active Directory (this user is a normal account that can be logged into – from a security perspective, it is recommended to disable this option). Meanwhile, employees with permissions to the newly created shared mailbox can access it alongside their own mailbox.
Easier management of shared mailboxes in Exchange is possible.
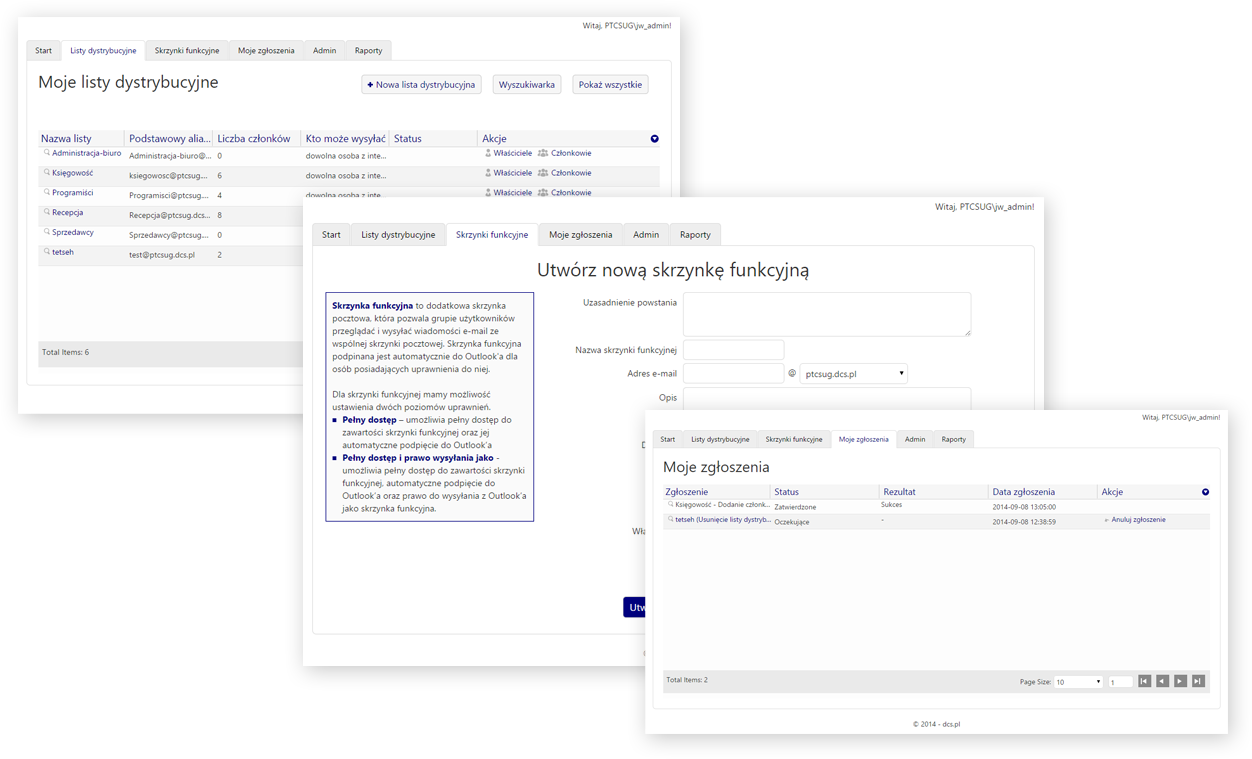
To simplify the management of distribution lists and shared mailboxes, Microsoft Exchange offers the DSM (Exchange Distribution List and Shared Mailbox Manager) application. The application consists of three main components:
- Web application for managing functional mailboxes and distribution lists
- All operations performed via the web interface cause:
- Direct changes to the database (e.g., adding a new shared mailbox in the database, updating the status, etc.)
- Queueing commands to Exchange/AD (executed as a PowerShell script through the task execution service)
- Database – an application database on the MS SQL server. The web application retrieves information from it for display and writes data to it.
- Windows Service – task manager executing periodic tasks
The software for managing distribution lists and shared mailboxes operates based on user roles, meaning the range of functions available depends on the login user’s permission level. Users can access it through a web browser – after logging in, they can, among other things...
- Browse and search for distribution lists and shared mailboxes
- Modify distribution lists and shared mailboxes for which the user is the owner
- Add new and delete existing distribution lists and shared mailboxes
- View open requests and those awaiting approval from the administrator
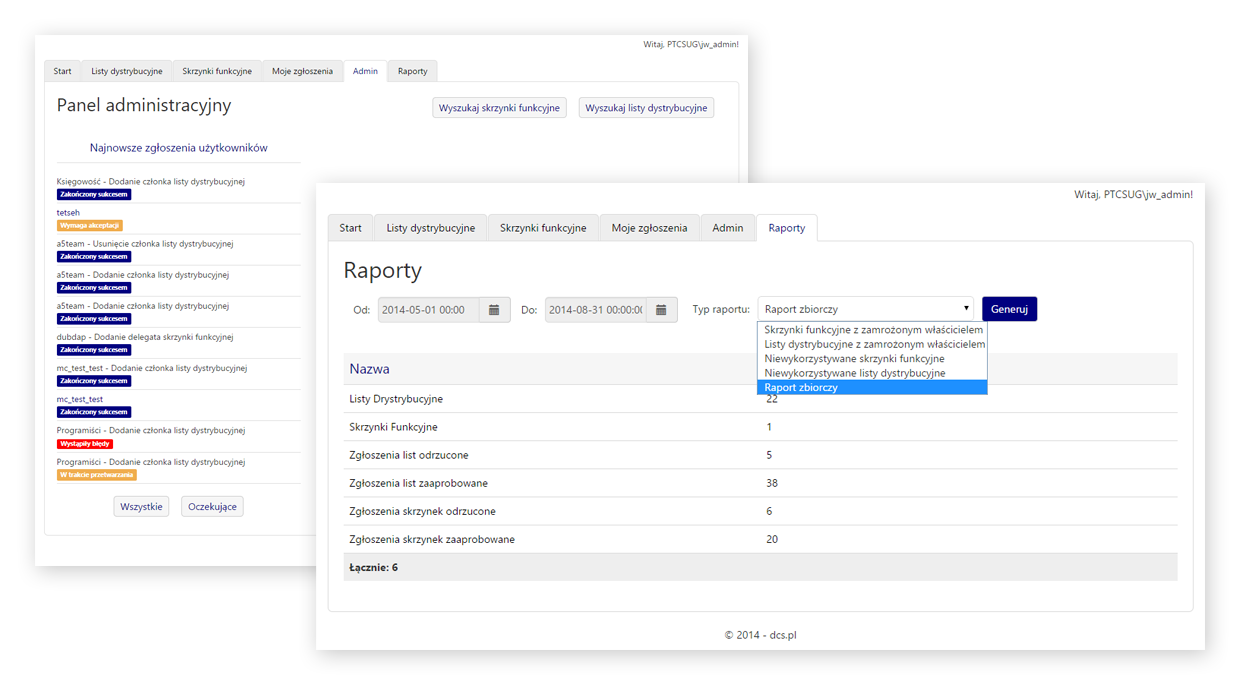
In addition to the permissions available to regular users, the administrator can also:
- Browse user submissions
- Accept or reject user submissions
- Search for and modify all distribution lists and shared mailboxes
- Generate reports showing statistics related to distribution lists and shared mailboxes for a given period


0 komentarze